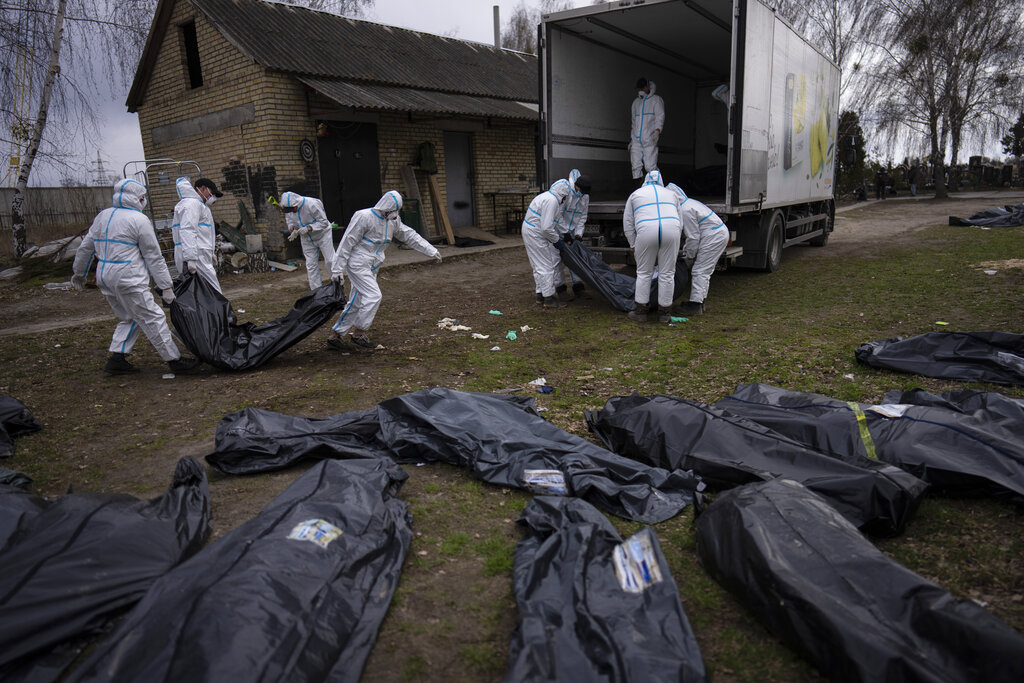
It is rarely in the best interest of the victim to pay ransom! Although the narrative often is “Because they have no choice” or “It is to protect people from the leak.” This is a complete myth, and it tends to be advanced by those who have paid ransom before, as a way of covering their terrible and avoidable behavior. Nobody owns this untrue narrative more than the insurance underwriters who normalized this behavior.
The problem with something like ransomware is that most companies are willing to pay ransom, and as long as this remains true it will be a persistent problem and only get worse. Ransomware has become so entrenched and is so easy and cheap to pull off, it will not subside until it becomes substantially difficult to succeed in a ransomware attack and make money doing so. Unfortunately, there have been no efforts to reduce ransom payments.
It is important to never forget exactly what is paid for, with money American companies pay
(Source)
When ransomware gangs lock down a system, they are frequently the first people the victims hear from and they will do their best to instill fear, create panic and make the situation seem much worse than it is. They will often claim that they will soon delete the data or raise their price for restoration. Paying for data restoration is never necessary, if even the most basic of precautions have been taken to back up data, but that is often not the cast and 80% of organizations facing ransomware do not have adequate backups. The situation is common, though always avoidable, and at least half of ransom payments are motivated primarily by the need to release systems and have data returned, not to avoid it leaking.
In many cases, companies have felt it was more reliable or faster to pay ransom, and with gangs so skilled at instilling fear and manipulating American companies, it is not uncommon. In some cases insurers have even insisted that victims pay ransom against their will. HSB is one of the few that still does this, forcing victims to pay ransom even if they felt it was not necessary, simply because the insurance company felt it was cheaper or safer to do so. However, the practice has never gone away completely from most insurers. Because the claims staff frequently receive kickbacks, they will tell organizations they are best off paying, even when they are not.
Unfortunately, it is not cheaper or safer to do so, and this is especially true if you do have backed up data. The restored data is 100% assured to be contaminated with malware and backdoors and the incident response will be far worse off. Paying ransom almost doubles the average cost of cleaning up an incident in the end. It also dramatically increases the chances of future attacks.
Continue reading →